Peter Ben Embarek (center) talks with Liang Wannian (left) and Marion Koopmans (right) after a press conference to wrap up a visit by an international team of experts from the World Health Organization (WHO) in the city of Wuhan, in Central China's Hubei Province. Photo: AFP
If WHO scientists cannot find the answer in China regarding coronavirus origins, maybe it's time for scientists to dig somewhere else and test more hypotheses to solve the mystery, Chinese scientists from the WHO-China virus tracing team suggested, after a joint WHO-China report on tracing the origins of coronavirus was released on Tuesday, which still leaves the virus origins question unanswered.The report, generated after WHO experts visited Wuhan, the Chinese city first reporting a COVID-19 case, dismissed the "lab-leak" conspiracy theory, and recommended transmissions between animals and humans, and transmissions through frozen food, which is consistent with what WHO experts said in a February conference in Wuhan. It also suggested the 7th Military World Games, which was held in Wuhan in October 2019, two months before the first case in this city was reported, is worth digging into.
Before official release on Tuesday, Western politicians and media once again cast the report, pre-leaked to media earlier, in doubt, questioning the investigation's transparency , impartiality and the involvement of Chinese government in the writing of the report. Chinese experts in this joint team refuted such baseless claims, saying the Chinese side has provided what it could, and it is willing to assist any further origins investigation in other places since it has mature technology on virus detecting and tracing.
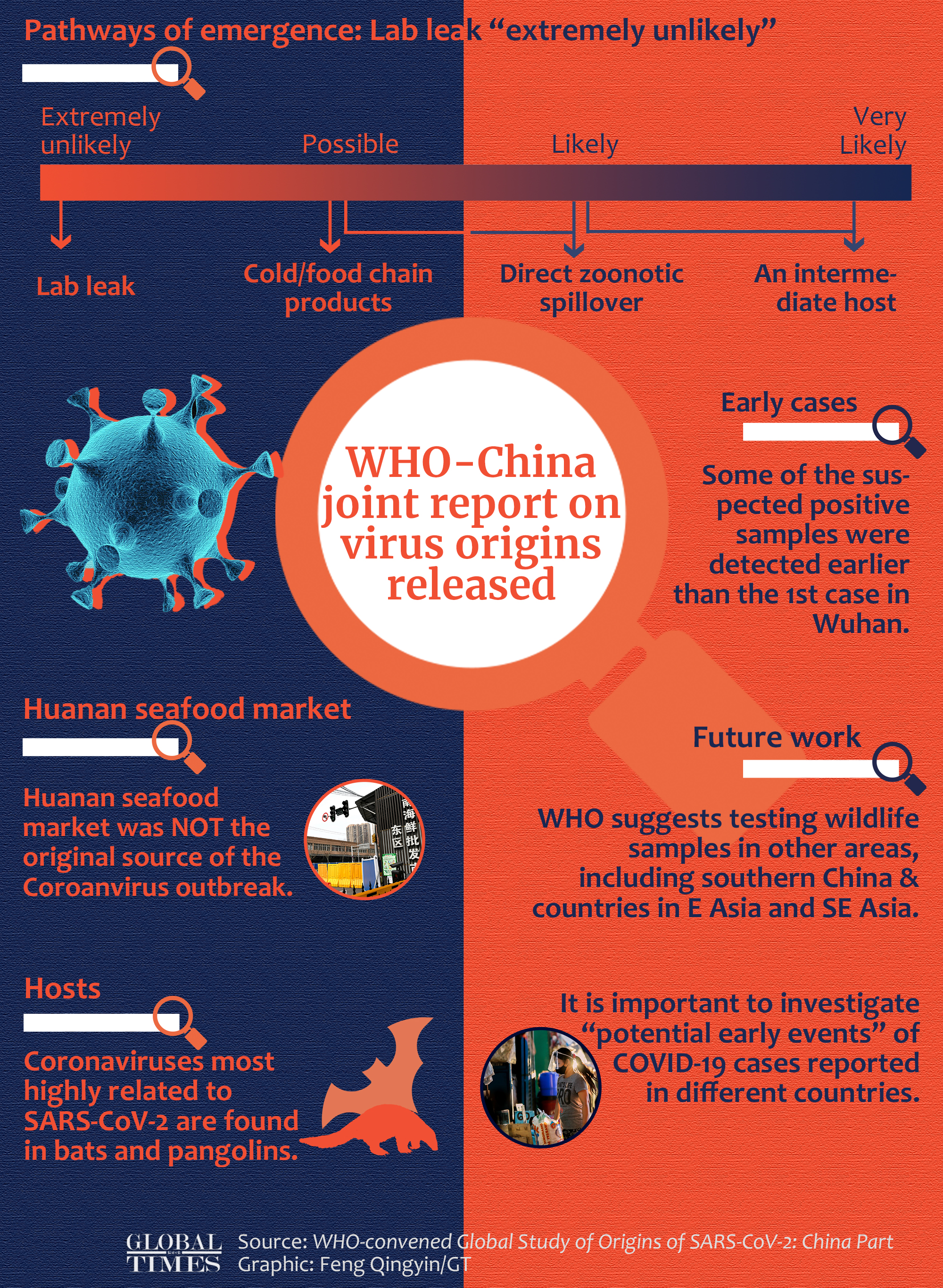
Highlights from #WHO-China joint report on coronavirus origins: -A lab leak was "extremely unlikely" -Huanan seafood market was NOT the original source of the outbreak -It's important to investigate "potential early events" of COVID-19 cases in different countries Graphic: Feng Qingyin/GT
The report pointed to a possible path of transmission between animals and humans and transmission through frozen food. It also said that the lab-leak theory is "extremely unlikely", which is consistent with what Peter Ben Embarek, a Danish food safety scientist leading the WHO team, said in Wuhan in early February, when wrapping up the WHO visit.
The Chinese Foreign Ministry said Tuesday night it appreciates the scientific, diligent and professional spirit of the WHO-China expert team and calls for further investigation in other countries and places to trace the virus origins as it is a global task after WHO released the joint report.
Politicizing the tracing work will only seriously hamper global cooperation on virus tracing, undermine global anti-epidemic efforts and lead to more loss of life. This runs counter to the desire of the international community to unite and fight the epidemic, FM said in a statement released on Tuesday night.
The WHO report also touched upon the hypothesis of the 7th Military World Games regarding virus origins, a possibility previously raised by a Chinese epidemiologist. The WHO report said that "no appreciable signals of clusters of fever or severe respiratory disease requiring hospitalization were identified during a review of these events," but recommended a further joint review of the data on respiratory illness from on-site clinics during the games.
"The hypothesis was raised by foreign experts during our communication," a Chinese expert from the joint team's animals and environment group told the Global Times. He said that large international events need to be considered as an option during origins tracing work of an epidemic.
The Chinese expert, who asked for anonymity, said that they obtained records from the Wuhan government, which show many countries had transported food to Wuhan during the event, many via cold chain route. "But now we only have records, no samples, so it will be difficult for us to find the evidence," he admitted.
The scientist also said it is highly probable that the virus was transmitted via cold chain, given the fact that cold chains triggered most of the later outbreaks in China after the one in Wuhan. "But at the early stage, all eyes were fixed on animals, so not enough samples were connected in the cold chain environment," said the expert, suggesting further research in this area.
The WHO report further suggests that animals in livestock farms in Southeast Asia could be "linked to early human cases" and that further study on these farms is needed.
The anonymous expert said that given the geographic adjacency and frequent exchanges between China and Southeast Asia countries, such a proposal is reasonable.
"Yunnan borders Southeast Asia, and bats travel frequently, which gives rise to the possibility of passing the virus to other animals and between each other," he said, noting that a batch of pangolins, which tested positive for coronavirus, were smuggled from other countries.
At a Friday conference, Feng Zijian, Deputy Director-General of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China's CDC), who is also the expert of the WHO joint team, said that there is a virus highly similar to COVID-19 in bats and pangolins in terms of virus sequencing. However, it's proven not to be a direct ancestor, while more animal species, including minks and cats, are worthy of inquiry as likely potential natural hosts of the virus.
According to the report, data suggests that the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan, where large clusters of infections were found, was not the original source of the outbreak.
"The place which saw the first outbreak does not necessarily make it the origins of the virus," another member of the joint expert team, who preferred anonymity, told the Global Times.
The expert said there's nothing strange about the fact that a scientific conclusion about the virus has yet to be found. On the other hand, it implies the difficulty in tracing virus origins. "Virus origins tracing work of previous large-scale epidemics was conducted by scientists in different countries and regions," said the scientist, urging global virus tracing, especially since mounting evidence suggesting that there were positive coronavirus samples found in other countries before the Wuhan outbreak.
He suggested further study of positive coronavirus samples found in human and environment before January 2020.
China has done what it can do in helping find the origins of the virus. If the answer could not be found here, maybe it's time to find it in other places, and test more hypotheses, according to the expert from joint team's animals and environment group. China is willing to assist virus origins tracing work in other places, as it has already grasped such technologies and methodologies, the expert said.
Doubt from West
Western media and politicians could not wait to fire torrents of criticism toward the report, which was leaked to some media before its publication.
Among the most vocal critics were US media outlets such as the New York Times and Washington Post, which questioned the report's impartiality as they hyped that WHO experts weren't given full access in Wuhan and the Chinese government exerted pressure on the UN body.
US Secretary of State Antony Blinken told CNN last week that he had concerns about "the methodology and the process," including "the fact that the government in Beijing apparently helped write it."
Such accusation was slammed by Zhao Lijian, spokesperson of China's Ministry of Foreign Affairs on Monday.
"The US kept showing its 'concerns' over the report. Is it attempting to exert pressure on WHO experts?" Zhao asked. "Please ask the experts which parts of the report the Chinese government helped them to write. Does China's facilitation on traceability research also behind-the-scenes manipulation?"
"What they needed, we gave them, including files," said the expert, explaining certain documents were restricted because it involved patients' sensitive personal information.
In an exclusive interview with the Global Times, Liang Wannian, team leader of the Chinese side of the WHO-China joint expert team, said that the Chinese side showed the WHO experts raw data one by one, such as the early case database and epidemiological survey forms of field use.
Foreign experts, including Peter Daszak, a British-born zoologist, who is president of the NGO EcoHealth Alliance in New York City, and Peter Ben Embarek from the WHO team, have repeatedly denied accusation of limited access in Wuhan.
Those Western countries only want WHO to pinpoint Wuhan as the origins of the virus, and better prove the virus was leaked from lab; if not, they just launched a smear campaign at China, said experts.




