SCI-TECH / AIR & SPACE
China plans to carry out near-Earth asteroid sample and return mission around 2025
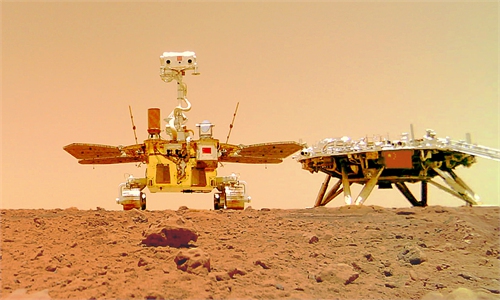
China's Zhurong rover sends back images from Mars. Photos: CNSA
China plans to carry out near-Earth asteroid sampling and return mission as well as the orbiting probe work of the main belt comet around 2025. And the sampling and return work of the Mars mission will also be carried out by around 2030, Xu Hongliang, the spokesperson of the China National Space Administration (CNSA), said at a press briefing in Beijing on Saturday.
China will also push forward the orbiting exploration of the Jupiter system and the planetary transit exploration mission. As for manned spaceflight, China will build long-term manned space station by the end of 2022 to carry out work involving the long-term stay of astronauts, space science experiments, and space station platform maintenance, according to Xu.
Xu revealed that China will launch the Chang'e-6 and Chang'e-7 lunar probes during the 14th Five-Year Plan period (2021-25), conducting missions such as environmental and resources exploration of the lunar polar regions, and polar region samples' retrieval. In the future, Chang'e-8 will also be launched.
In December, China's Chang'e-5 safely landed at its designated landing area in North China's Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, marking the successful completion of the country's first ever lunar material retrieval mission.
In May, China successfully landed a spacecraft on Mars, becoming the second country in the world to successfully deploy a robotic rover onto the surface of Mars after the US.
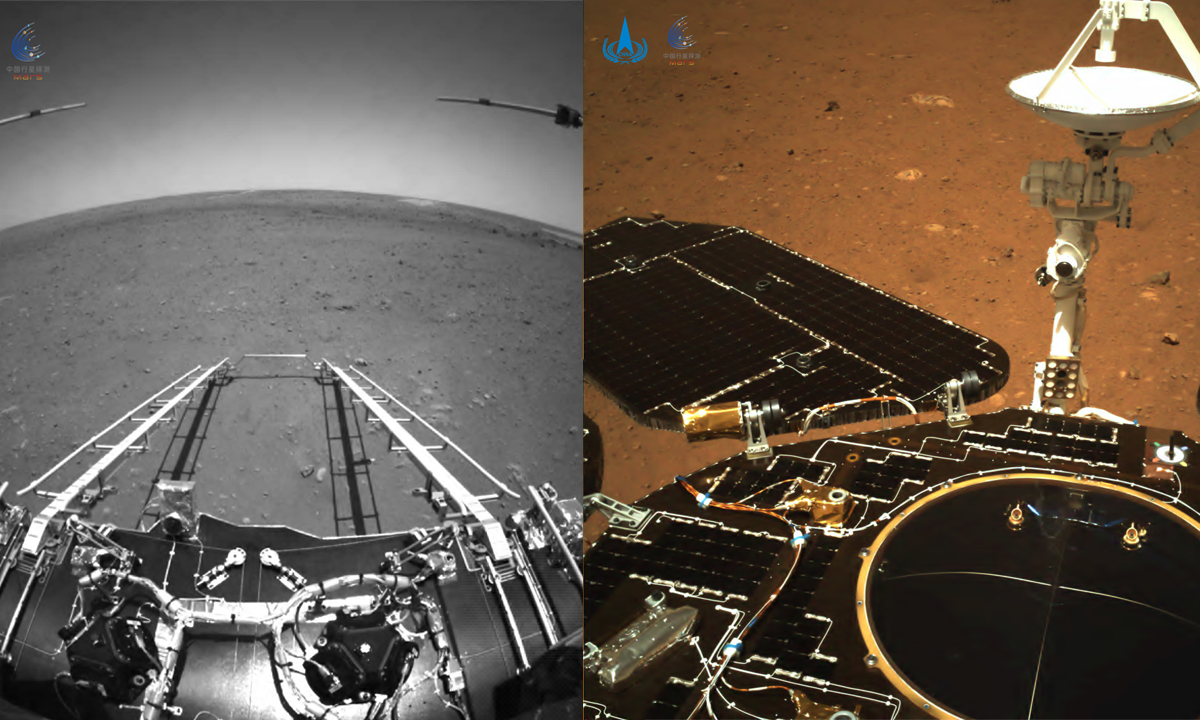
On Friday, China unveiled the first reel of images from the Tianwen-1 spacecraft's landing on Mars.
Liu Jianjun, the chief designer of the ground application system for China's first Mars exploration mission, said at the press briefing that the country is expected to form a deep understanding of the characteristics and evolution of the paleoenvironment on Mars, and study the planet's livable environment.
Six scientific instruments, including the Mars rover radar, magnetic filed detector, and composition detector, have been equipped on the Mars rover to test and obtain exploration data, according to Liu.
China in recent days has been cooperating with the United States National Space Administration (NASA) and the European Space Agency (ESA) regarding the Mars rover orbit data exchange, to ensure the safety of the on-orbit satellite of the Mars rover, said Xu.
During the Tianwen-1 Mars exploration mission, CNSA has cooperated with four space agencies including the European, French, Argentinean, and Austrian on loads, testing and other support. Meanwhile, China has been keeping in communication with French, Austrian and Russian organizations on the application and cooperation of Mars probe exploration data.
"It has become an international norm to conduct international cooperation in lunar and deep space exploration. China will hold an open attitude, and carry out wide cooperation based on the principle of achieving shared growth through discussion and collaboration regarding the development of sectors such as lunar exploration, asteroid exploration, and the international lunar research station," Xu said.
Global Times