IN-DEPTH / IN-DEPTH
FAST FACTS: The ‘Sequelae’ After Loosening Anti-Virus Measures In Europe
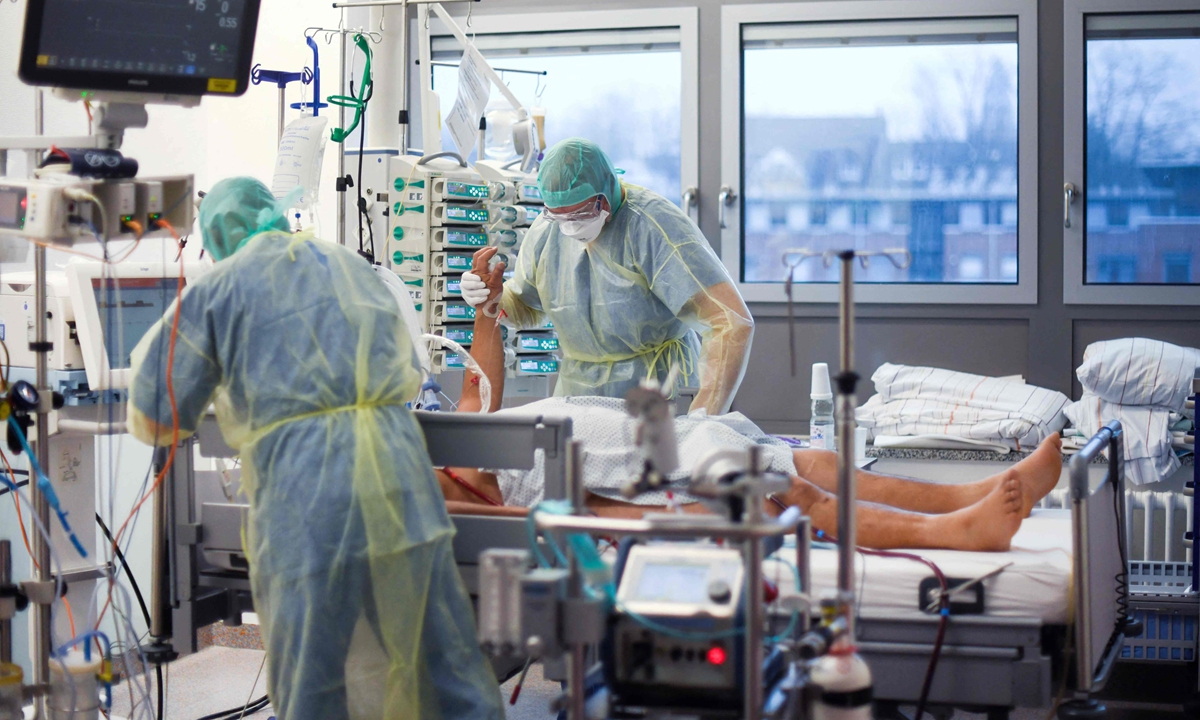
Medical staff assist a patient infected with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit of a hospital in Bochum, Germany, on December 16, 2021. Photo: VCG
At present, COVID-19 is still raging around the world. The World Health Organization recently emphasized that theCOVID-19 epidemic is still a "public health emergency of international concern," and repeatedly urged governments around the world to remain vigilant and be fully prepared in epidemic prevention measures. However, some countries and regions have removed such epidemic prevention measures and adopted the "coexistence with the virus" model.
At present, the "sequelae" of this model are gradually emerging. In some countries and regions, including European countries, the number of cases has surged, the death toll has risen, and medical systems are under enormous pressure. To this end, many public health experts around the world have advised that "public health measures should be rebuilt instead of letting the public take the risks of their lives."
UK
Since announcing the commencement of a "living with COVID" era in February and the removal of a series of virus prevention measures, a surging number of cases is deepening the crisis in the health service. In March, COVID-19 infections in the UK had climbed to 1 million in a week, official statistics show. One in nine people (6.4million) were waiting for elective operations such as hip and knee replacements and cataract surgery by March - up from the 6.18 million similarly stuck in February, according to Daily Mail.
Germany
Governments across Germany made an agreement in February to gradually loosen the country's virus prevention policies, including the order to ban unvaccinated people from entering public venues. However, in mid-March, the new cases in a week broke a new record at 2.6 million. Due to the pandemic, 60 percent of German hospitals have had to postpone scheduled surgeries, while six out of 10 hospitals are experiencing nursing staff shortages.
EU
The European Commission said in April that between 60 and 80 percent of the EU's entire population was estimated to have been infected with COVID-19.
Eurostat said on April 22 that in the first quarter of this year, the GDP of the 19 member states of the eurozone had grown by 0.2 percent, compared with a 0.3 percent increase in the previous quarter. However, the French economy stagnated in the first quarter, while Italy's economic output contracted, and Spain's economic climb lost its footing.