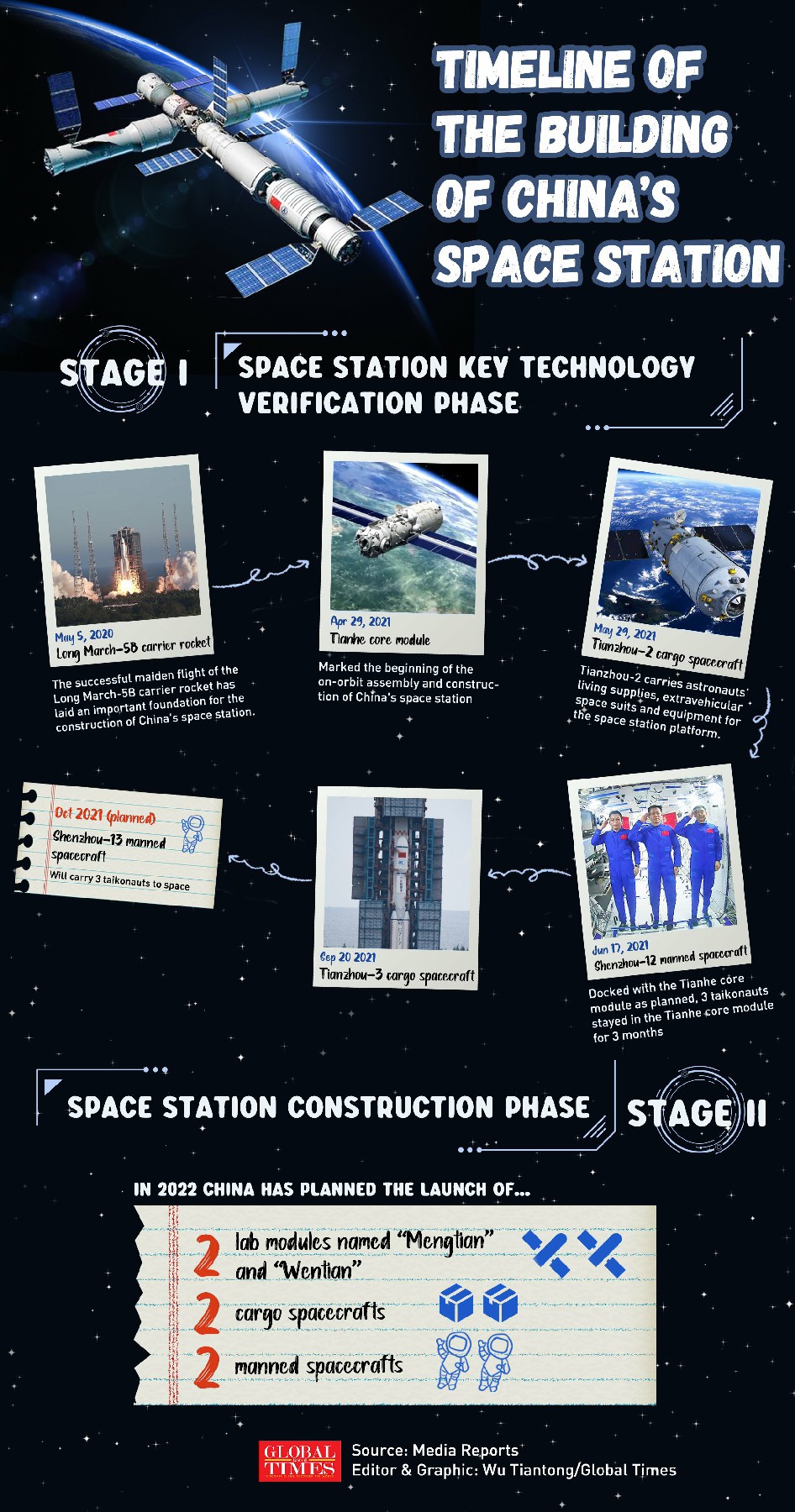
China successfully launches Tianzhou-3 for second space station supply mission; to support upcoming six-month Shenzhou-13 manned mission
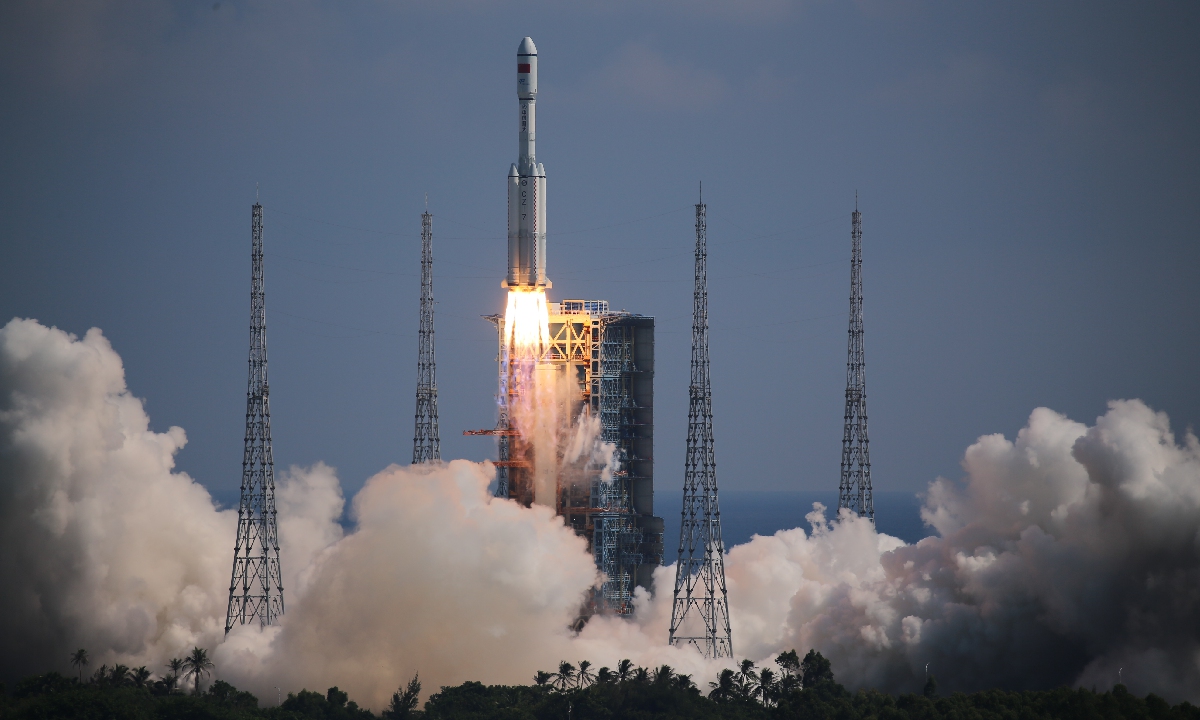

Photo:Hu Xujie
Knock knock. This is your delivery-man Tianzhou-3, and please confirm your package receipt and may you have a happy Mid-Autumn Festival!
Carrying the Tianzhou-3 cargo spacecraft, the Long March-7 Y4 rocket lifted off from Wenchang Space Launch Center located in South China's Hainan Province on Monday afternoon, one day ahead of this year's Mid-Autumn Festival - one of the happiest family reunion holidays for the Chinese people.
The lift-off gave the nearby forest of coconut trees quite a shake in the Hainan tropical haze, the same way it excited many who came to witness the historic moment at the Wenchang beach on Monday afternoon.
As the fourth of 11 missions scheduled to build China's three-module space station, Tianzhou-3 mission came shortly after the historic Shenzhou-12 mission in which three taikonauts spent a record 90 days in the China's space station core module and safely returned to Earth on Friday.
After a flight time of around 597 seconds, the spacecraft separated with the rocket and entered preset orbit. At 3:22 pm, the solar panels onboard the spacecraft smoothly unfolded, with all functions in normal operating condition, marking the success of the third launch of a spaceship to the space station core cabin, according to the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA.)
The Monday mission is tasked to bring supplies, equipment and propellant to get Tianhe ready for the next three-taikonaut Shenzhou-13 mission in October for their six-month stay. It is the Tianzhou spacecraft series second supply delivery run to the orbiting Tianhe module following a first by the Tianzhou-2 mission launched on May 29.
Although the launch of Tianzhou-2 by Long March-7 Y3 rocket was a successful one, it experienced two delays and met problems of leaking of injected fuels.
The Tianzhou-2 cargo spacecraft was originally slated to be launched at around 1:30 am on May 20 and to head to China's Tianhe space station core cabin, which was launched into orbit on April 29, for a supply run. However, the launch was scrubbed narrowly following an announcement from CMSA on the early morning of May 20 for "technical reasons."
Research teams were dispatched immediately to check system functions, while the command center prepared for an attempt to recover the mission, which had been set to a day later in the early morning of May 21. However, after liquid oxygen was refueled eight hours before the scheduled launch time, abnormal signals once again occurred.
Drawing lessons from the previous launch, the Long March-7 rocket developer with the China Academy of Launch Vehicles have further optimized the quality examination process before and after the lift-off and make detailed emergency plans. This is to ensure the launch mission is on time with zero errors, the academy told the Global Times on Friday.
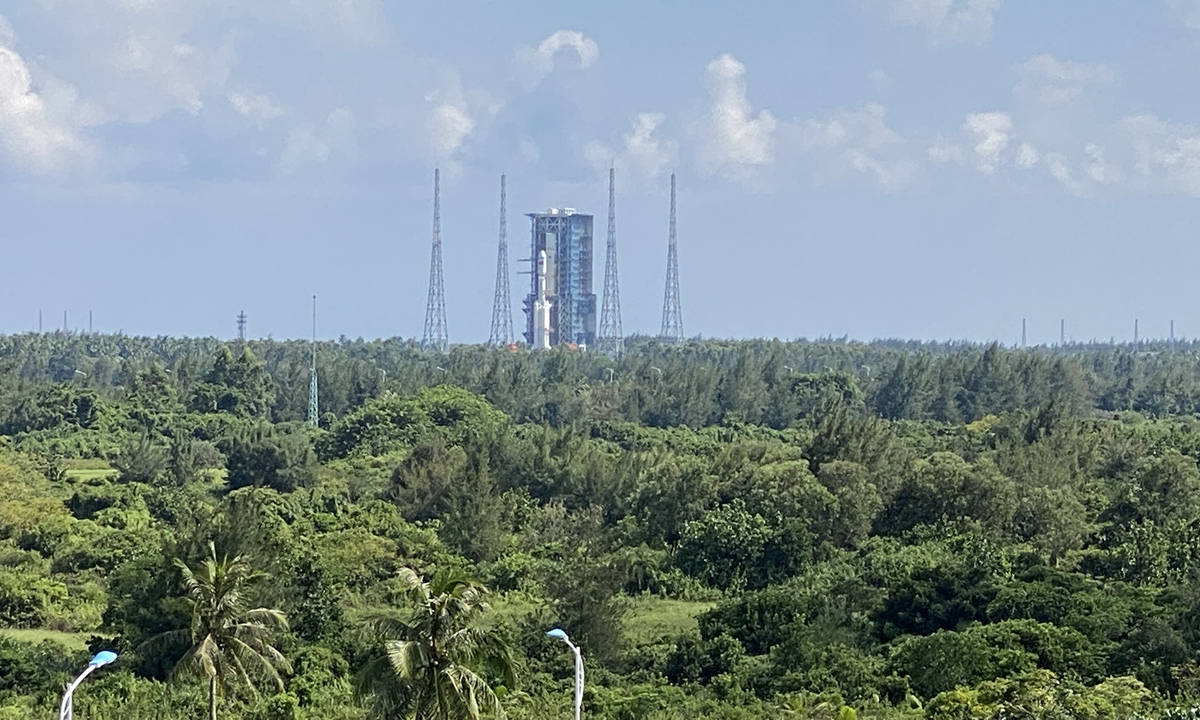

Photo:Deng Xiaoci/Global Times
To sustain Taikonauts' longer stay in spaceGlobal Times learned from the mission insiders that Tianzhou-3 mission will lay ground for the upcoming October Shenzhou-13 mission, just the way Tianzhou-2 mission prepared for the epic Shenzohu-12 manned spaceflight mission. The October mission is expected to last six months, renewing the record of the longest stay in space for a Chinese astronaut in a single mission.
The spacecraft developer China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) told the Global Times in a statement that just like the Tianzhou-2, Tianzhou-3 will carry a range of goods including daily necessities, drinking water, gas supplies, consumables for extravehicular activities [spacewalk,] as well as experiment payloads.
Yang Sheng, Chief designer of the Tianzhou-3 spacecraft system, told the Global Times that "As Tianzhou-3 mission will sustain taikonauts' 6-month-long stay in space, the density of cargo is greater on Tianzhou-3 than on Tianzhou-2, and Tianzhou-3's loading capability is also higher than that of Tianzhou-2. The number of packages onboard Tianzhou-3 is 25 percent more than on Tianzhou-2."
There were 6.8 tons of supplies onboard the Tianzhou-2, including some 160 parcels of goods and two tons of propellants, CAST told the Global Times previously.
One of the most expensive items to be onboard the Tianzhou-3 would be one piece of spacesuit specially designed for spacewalk missions that weighs some 90 kilograms, the CAST highlighted in the Friday statement. Tianzhou-2 had sent two pieces of spacesuits for Taikonauts' spacewalk with each weighing some 100 kilograms.
Also, onboard Tianzhou-3 is the replacement parts of the urine treatment system to ensure the device is in the best condition for the Shenzhou-13 crew, Global Times learned from the system developer 206 Research Institute of the Second Academy of the China Aerospace Science and Industry Corp (CASIC).
"The system has processed some 600 liters of urine into over 500 liters of water which was used to generate oxygen and for clean-up purpose during the Shenzhou-12 crew's three-month stay. Shenzhou-13 crew will install those parts when moving into the China's space station core module," Cui Guangzhi, the project leader, told the Global Times.
The Tianzhou-3 cargo spacecraft is expected to also execute a fast and automatic rendezvous and docking with the Tianhe core module, just like the Tianzhou-2 spacecraft did in May, which took some eight hours after lift-off,according to Deng Kaiwen, assistant of the Tianzhou-3 cargo spacecraft's chief commander from the spacecraft developer
Compared to the Tianzhou-1's rendezvous and docking with Tiangong-2 in 2017, which took about two days, Tianzhou-2 took a mere eight hours to achieve the feat in May.
Tianzhou-3 will dock to the Tianhe module from the rear. Before such development, CMSA updated on Saturday, Tianzhou-2 had flown around Tianhe and conducted an automatic docking to the craft's front, which took four hours.
Shenzhou-13 will later rendezvous with the Tianhe module and conduct a R-Bar or vertical docking with the orbiting craft, which Shenzhou-12 had practiced on Friday before heading back to Earth.
Graphic: Wu Tiantong/GT




