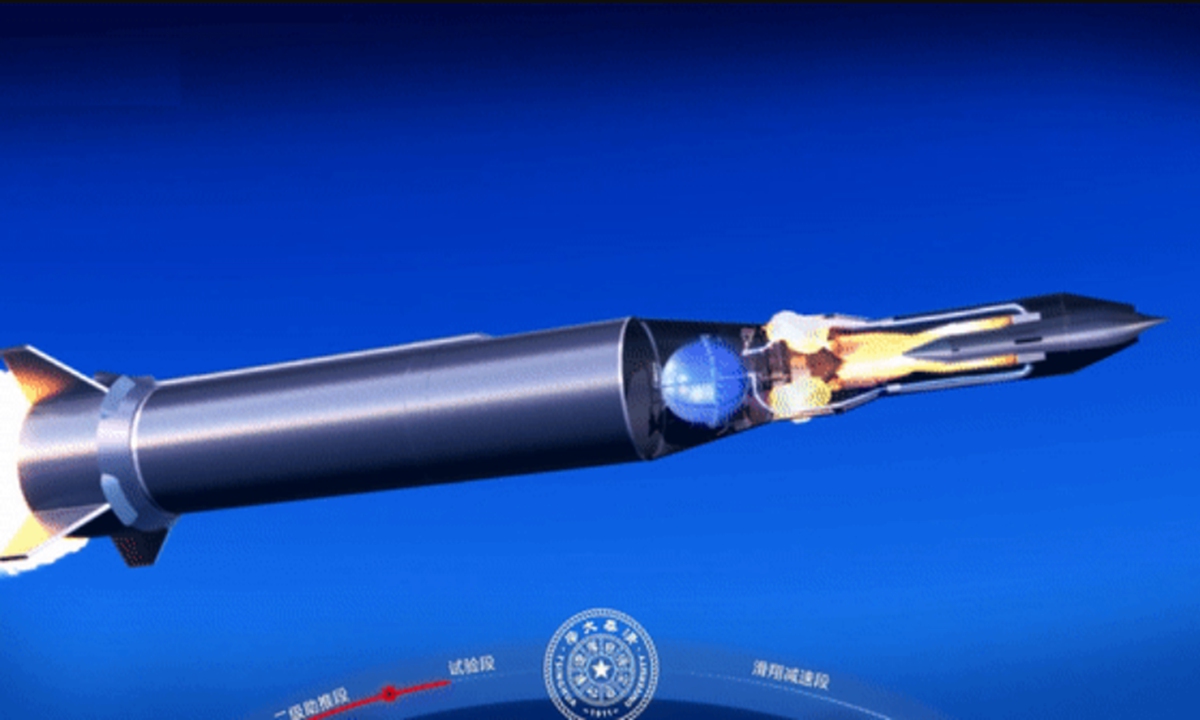
A new engine independently developed by China conducts a test flight on January 24, 2022. The engine was sent to a predetermined height and velocity by a two-stage rocket booster, before it started to breathe in air, ignite its combustion chamber, and provide constant thrust, marking the success of the test. Photo: Screenshot from China Central Television
China on Monday conducted a test flight for a new engine that experts said could power China's future hypersonic aircraft and near-space plane.
The engine, developed by the Laboratory of Spray Combustion and Propulsion under School of Aerospace Engineering at Tsinghua University, successfully conducted a flight test on Monday morning, China Central Television (CCTV) reported.
A two-stage rocket booster was used to assist the test flight, CCTV said, noting that after the separation of the first stage, the second stage sent the engine to the predetermined height and velocity, and that was when the air inlet of the engine began to breathe in air very efficiently, and the fuel supply system began to spray vaporized jet fuel into the combustion chamber.
Then the ignition system started properly, the combustion chamber entered combustion status as planned, the engine worked in a stable manner and provided constant thrust, marking the complete success of the test flight, CCTV reported.
A computer-generated video shows that the second stage rocket booster did not separate from the engine, and it opened a parachute to land in a desert area, so it could be recovered.
The test gathered data on the effects caused by the parameter changes of the working environment to the operation characteristics of the engine's combustion chamber under real flight conditions, the report said.
It also thoroughly tested the engine's real work characteristics, validated the practicability of the technology and provided test data and accumulated experience to make this new technology into products, CCTV said.
This achievement will further enrich China's aerospace capabilities, and has strategic significance in new-type propulsion, the report said.
Huang Zhicheng, a senior expert on aerospace science and technology, told the Global Times on Monday that the experiment is about the engine's hypersonic flight.
Judging from the descriptions on how the engine worked, it is likely a scramjet engine, which is one of the key technologies to achieve hypersonic flight, experts said.
Wang Ya'nan, chief editor of Beijing-based Aerospace Knowledge magazine, told the Global Times on Monday that since the engine needed a two-stage rocket booster, it probably worked near space or in the upper edge of the atmosphere where air is very thin, with insufficient oxygen to support combustion.
Under such circumstances, airflow needs to be slowed down after it enters the inlet to blend it with the fuel, where fuel vaporization is a good idea to apply as it can blend the fuel and air very well to guarantee stable and effective combustion, Wang explained, noting that this could be the breakthrough in the test.
Li Xiaoguang, an expert on intelligent unmanned systems at Qingdao University, told the Global Times that the CCTV report did not reveal the specifics of the engine, but it seems to be no more than one meter long according to the report, so its thrust would not be very high.
"If it is a scaled model test which aims to verify the theory, it means that there is still some way to go before the technology matures and becomes a real product," Li said.
When the technology becomes mature, it could see applications on hypersonic aircraft and near-space plane, Wang predicted.




