Chinese cities race to experiment autonomous driving, ready to accelerate commercial use
China’s advantages lie in top-level design, large market, and complete industrial chain
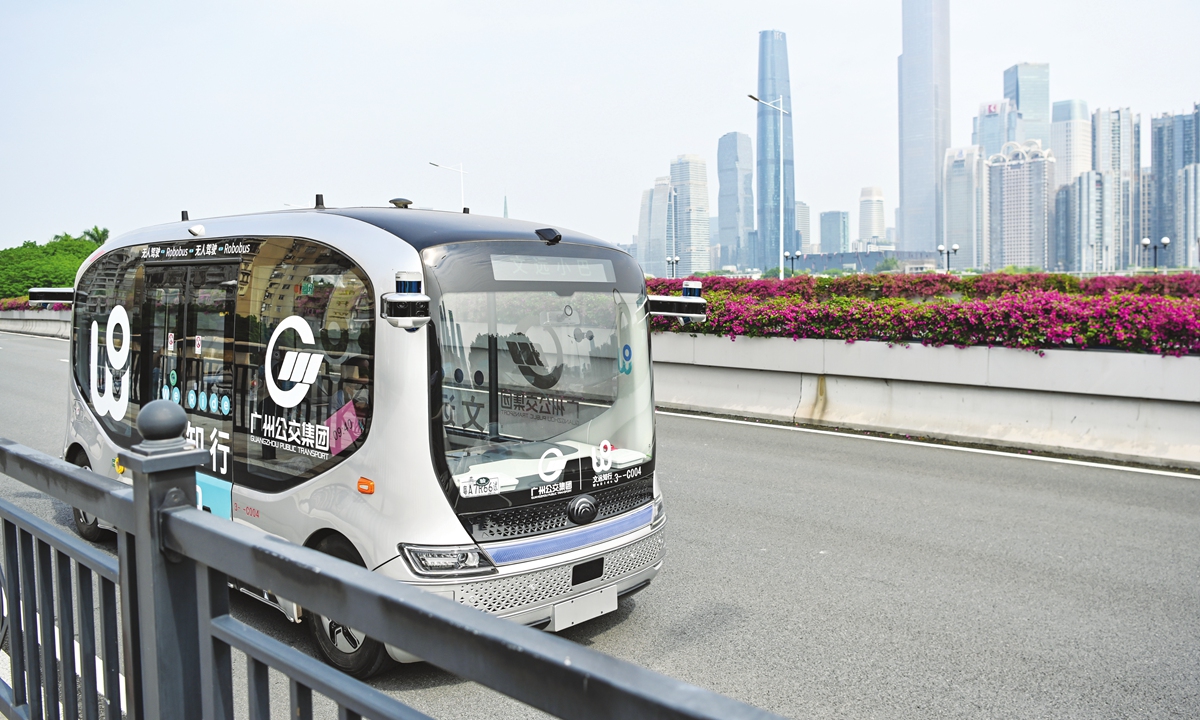

An autonomous driving bus in Guangzhou Photo: VCG
Don't get surprised if a visitor board a taxi or bus in Shenzhen, a tech hub in South China's Guangdong Province, and can't find a driver. Nowadays, more cities in China are offering driverless public transport, reflecting the rapid growth of autonomous driving in the country.And, Beijing city announced on Friday the launch of the phase-3 construction of Beijing High-level Autonomous Driving Demonstration Zone.
As part of phase-3, the demonstration zone, now covering only 60 square kilometers, will be gradually extended to a larger zone of 500 square kilometers, according to an official at the 2022 World Intelligent Connected Vehicles Conference.
In August, the Ministry of Transport released a set of national guidelines to encourage the use of self-driving for taxi fleets under given conditions, a move that industry analysts said will help speed up the commercialization of autonomous vehicles in China.
Prior to the above developments, autonomous driving has been accelerated in other places.
On July 20, Beijing city launched China's first commercial operation of driverless travel service. In August, Southwest China's Chongqing city and Central China's Wuhan city came out with new policies for autonomous driving commercialization, allowing driverless vehicles to carry out commercial services on public roads, and issuing licenses to the country's first batch of driverless demonstration operations.
"Government policies have played a strong role in promoting the development of autonomous driving in China. The country's autonomous driving sector emerged a little bit later than the US and Europe, but has accumulated strong growth momentum," Zhang Xiang, visiting professor at Engineering Department of Huanghe Science and Technology University, told the Global Times on Sunday.
China already has a top-level design in the autonomous driving industry chain. The 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-25) details the scientific and technological blueprints for quantum communication, 5G/6G, blockchain distributed systems, industrial Internet of Things, semiconductors, and the new-energy vehicle (NEV) industry chains.
The automatic driving industry chain should combine the future industry chain of the new generation communication network, distributed system, smart city planning, and NEV, forming a one-stop comprehensive application scenario, and its future is unlimited, Chen Jia, an independent research fellow on international strategy, told the Global Times on Sunday.
"On the macro level, autonomous driving industry chain can be used to further improve urban infrastructure, accelerate the optimization of urbanization process and cope with the challenges of population aging. On the micro level, it can drive the development of urban science and technology industry cluster centering on intelligent driving," said Chen.
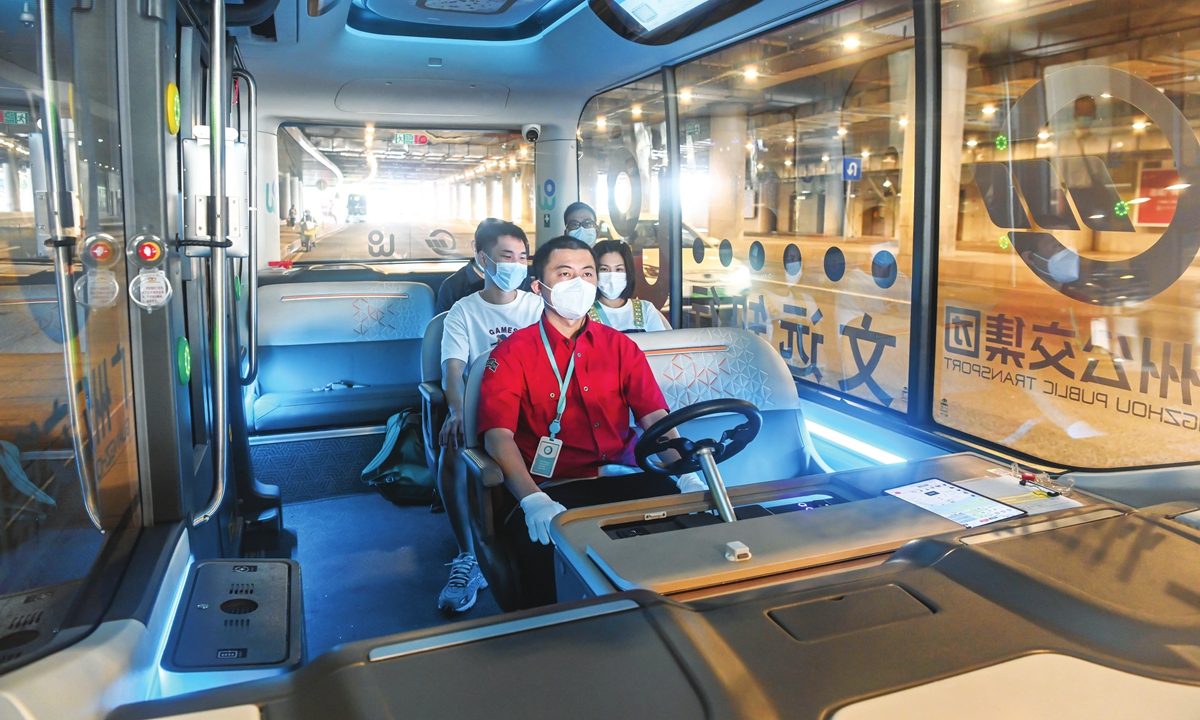

Passengers in an autonomous driving bus in Guangzhou Photo: VCG
Unique advantages
There is no need to underestimate China's unique advantages in autonomous driving, which is likely to become an important pillar for the development of global autonomous driving technology in the future, noted Chen, whose insight is echoed by industry insiders.
"There is no problem with Chinese technology, which is now able to position cars on roads by the centimeter-level of accuracy," an engineer at a Shenzhen-based high-precision positioning system software company, told the Global Times.
Positioning is an important part of autonomous driving technology, including path planning, connection with urban transport network and other functions, which requires accurate positioning, the engineer said, adding that the company is a supplier to about 80 percent auto manufacturers in China and is now seeking overseas expansion.
Radar, or LiDAR, is the eye of a vehicle and an essential part for information acquisition in autonomous driving. China is now advanced in this aspect, a manager of a Shanghai-based radar producer told the Global Times on Sunday.
And the competition among domestic car radar manufacturers is very fierce, the technology's iteration speed is also fast, the manager noted.
Vehicles with intelligent functions are mostly NEVs Since China's NEV is leading in the world, the cost of autonomous driving could be far lower than other countries, and marketed earlier than foreign brands, said Zhang.
For example, Baidu, for example, announced that its self-driving cars could be sold for 350,000 yuan ($50,090) each.
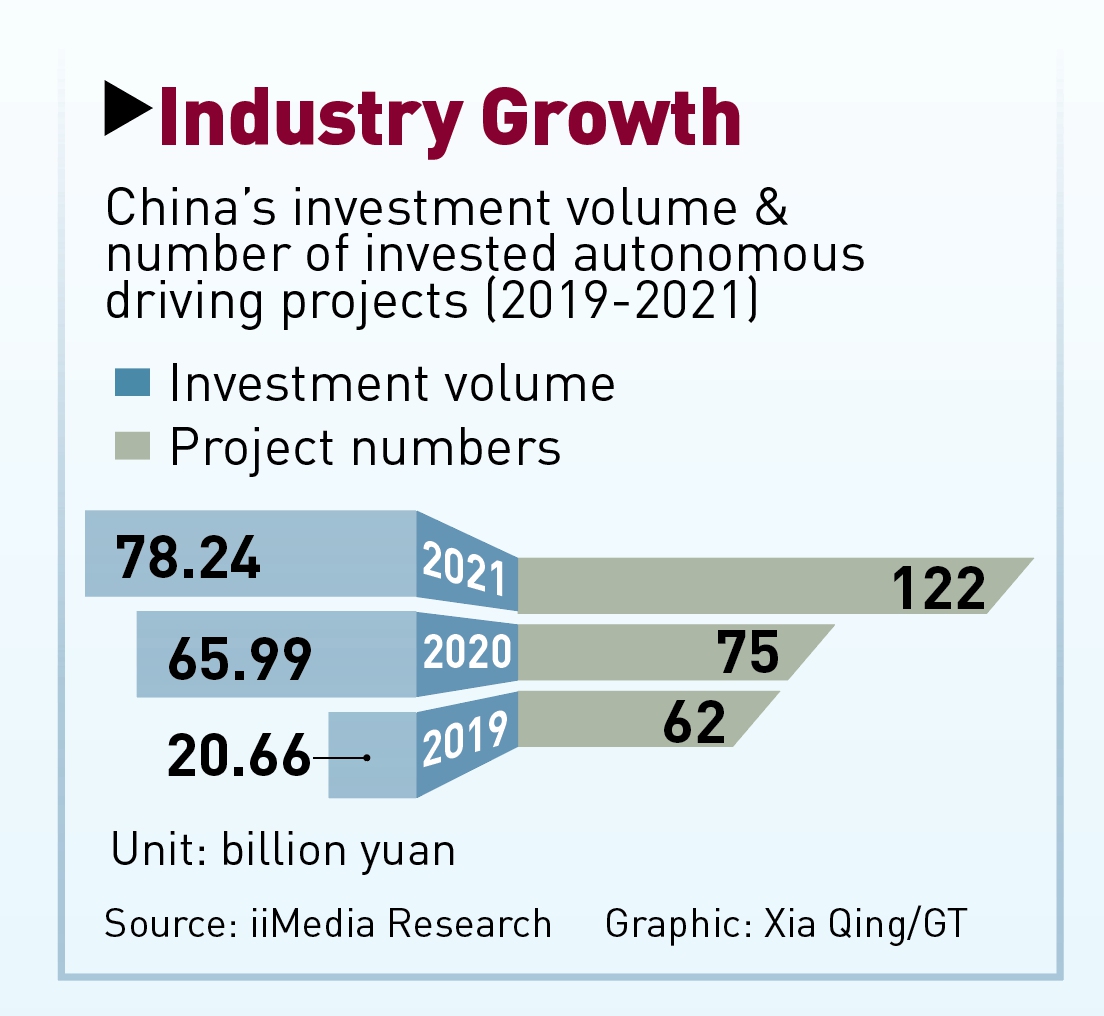
Graphic: Xia Qing/GT
Fierce Competition
According to statistics released at the 2022 WICV, 2.88 million passenger cars with driver assistance functions were sold in China in the first half of this year. They accounted for 32.4 percent of all passenger car sales in the country during the same period, rising 46.2 percent year-on-year.
There were 10.99 million NEVs running on China's roads at the end of August this year, statistics from the Ministry of Public Security showed.
"China has a huge market and could bring great economic benefits," Zhang said.
At present, autonomous driving globally has not yet entered large-scale operation. Most countries remain in the pilot application stage, while the majority of current application scenarios are in public transport, such as buses, said Chen.
"In China, the development path of commercial operation of autonomous driving service is likely to start with specific bus routes in cities," said Chen.
This can be seen from the first batch of pilot applications of intelligent transportation projects, including 14 autonomous driving projects, approved by the Ministry of Transport on Wednesday, and those projects will last until December 2023.
Guangzhou city was one of the designated experimental cities. A total of 50 autonomous buses will be put into operation on certain routes, with a cumulative mileage of no less than 1.5 million kilometers. Meanwhile, 210 autonomous passenger vehicles will also be put into operation in its high-tech demonstration zones, providing no less than 300,000 trips and running for no less than 200,000 hours.


