From prevention to treatment, COVID diagnosis and treatment protocol pursues 'optimal solution': Global Times editorial
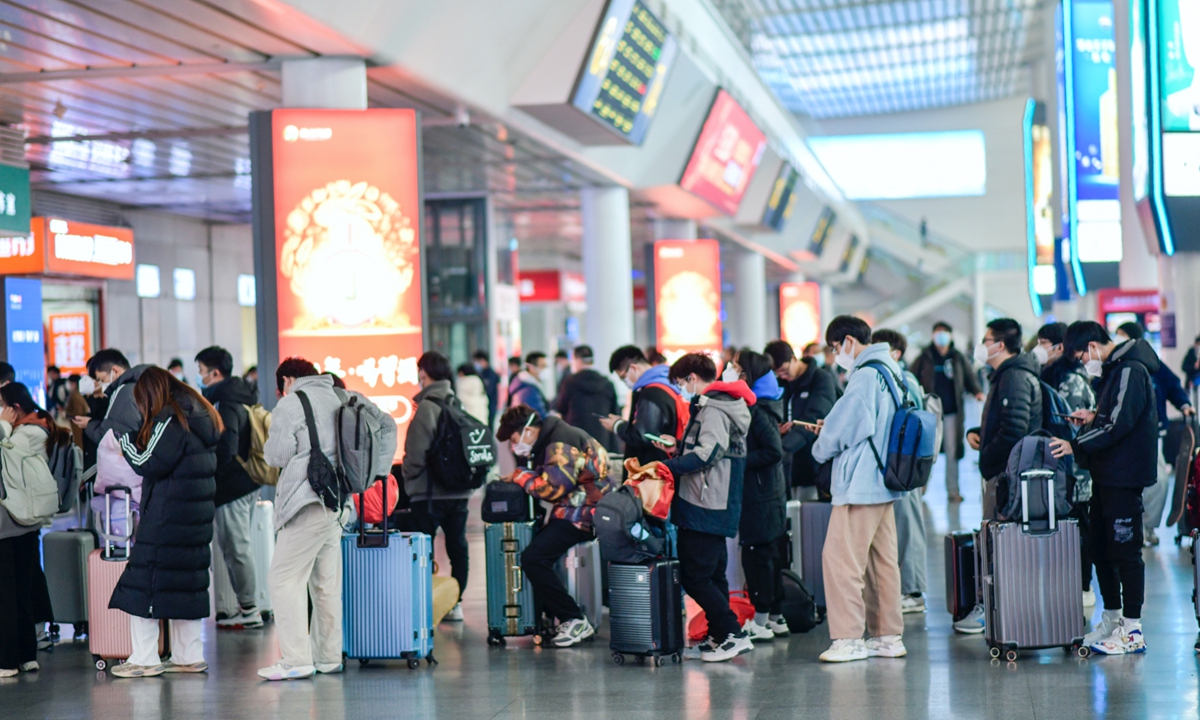

Long lines are seen back at a train station in Jinan, East China's Shandong Province, on December 7, 2022, as China further optimized COVID response and relaxed controls. Photo: IC
China's National Health Commission (NHC) and National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine published the 10th edition of the diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 on Friday. This is the NHC's first national guiding protocol after China announced to downgrade management of COVID from Class A to Class B from January 8. The 10th edition fully embodies the principle of Class B management for Class B infectious diseases. It lays an important foundation for further scientific and standardized COVID diagnosis and treatment, ensuring the smooth and orderly transition of epidemic prevention and control into a new period after going through its peak.
It has been nearly a year since the 9th edition of the diagnosis and treatment protocol for COVID-19 was released. The focus of China's epidemic prevention and control has changed from preventing infection to protecting health and preventing severe cases. Prior to this, many hospitals in Shanghai, Beijing, Southwest China's Sichuan Province and other places had successively released their own diagnosis and treatment plans to further optimize the clinical process. At the same time, many medical professionals expressed their hope for a nationwide version of the diagnosis and treatment protocol. It should be said that the 10th edition released by the NHC has brought together the strengths of different versions, helping to promote good experiences and practices to the whole country. It has important guiding significance for small cities and remote rural areas.
Compared with the previous nine editions, the biggest change in the 10th edition is the shift from prevention to treatment. It has several outstanding features. First, it emphasizes efficiency. For example, according to the new edition, hospitals will no longer tally suspected cases, testing positive using antigen test kits was added as a criterion for confirming infections, and the standard used for discharging patients from hospitals has been adjusted. These can improve the efficiency of clinical diagnosis and treatment and better achieve rapid hospital admission. Second, it emphasizes early action, including listing finger blood oxygen saturation and other indexes as warning signs of worsening conditions, further improving the diagnostic criteria and warning indicators for severe and critical cases. It will help with early detection, early identification, early intervention and early referral.
Third, it emphasizes accuracy, including adjusting the name of the disease, optimizing "clinical classification", and using "infection" instead of "pneumonia" to define the scope of diagnosis and treatment, which is more in line with the reality of clinical practice. Fourth, it stresses combination, such as strengthening the concept of treatment of both COVID and patients' underlying health conditions, as well as joint treatment with Chinese and Western medicine.
It is not difficult to see that the new version of the COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment plan focuses on vulnerable groups such as the elderly, children, and people with underlying diseases. Its target is very clear - preventing and reducing the occurrence of severe cases to the greatest extent possible, which is also the focus of Class B Management.
Affected by factors such as mobility, density, and immunity levels of the population, various regions may face pressure from the epidemic in the near future. In this regard, the scientific and professional nature of the 10th edition of the diagnosis and treatment plan is a realistic response to the urgent demands of society. It reflects the consistent adherence to "People First, Life First" under the new situation of Class B Management.
Since the release of China's first version of the diagnosis and treatment plan in January 2020, each updated edition has seen obvious changes, which is precisely the main thing they all have in common, that is, coping with the uncertainty of the epidemic in accordance with the time and situation under a stable guiding principle, scientific methods, and flexible diagnosis and treatment measures. They are also important footnotes in China's epidemic prevention and control process. Looking back, each version of the diagnosis and treatment plan achieved the "optimal solution" under the conditions at that time. Facts have proved their scientific nature and effectiveness, and they have also been recognized by society.
With Class B Management about to be formally implemented, we can see that a lot of preparation work is taking place, and the introduction of a new version of the diagnosis and treatment plan is only one aspect of it. Many provinces and cities including Beijing, Tianjin, Chongqing, Fujian and Guizhou have formulated and issued specific implementation plans for Class B Management focusing on protecting people's health and preventing severe cases in accordance with local situations, such as improving the monitoring and early warning system, implementing a tiered treatment system, and setting up as many fever clinics as possible. China is proving through concrete actions that Class B Management is by no means the same as giving up.
By combining the concept of "People First, Life First" with our institutional advantages, the energy being released is huge. This has been fully proven in the practice of the past three years. This advantage will continue to play a decisive role under the major adjustment of Class B Management. We firmly believe that China has the ability to ensure the smooth and orderly transition of COVID-19 response phases, protect people's life and health to the greatest extent while minimize the impact of the epidemic on economic and social development.